|
Return to your Search Results
Return to Search page
Search the Noteworthy Practices database
Michigan Undertakes Initiatives to Encourage a Data-Driven Approach to Local Roadway Safety
Publication Year: 2014
Background
To maximize returns on investment in preparing, utilizing, and maintaining a strong safety data system, the Michigan Department of Transportation (MDOT) has undertaken a number of programs that make use of roadway, traffic, and crash data to improve safety on local- and State-owned roads in the State of Michigan.
Like many states, Michigan faces the challenge of addressing a large number of fatal crashes on non-State-owned highways, which comprise roughly 90 percent of the roadway miles and the majority of roadway fatalities in Michigan. To improve safety on local roads, Michigan has participated in several initiatives that help bolster the State's multifaceted roadway safety program by providing local agencies with meaningful, timely access to crash data, as well as tools for data analysis and training to manage their safety processes.
The Practices
- Local Safety Initiative - A technical assistance offering, MDOT provides participating local agencies, as part of the Local Safety Initiative, with site-specific analysis, including ranking reports for intersections and segments. At no cost to local agencies, MDOT staff visit the agencies to conduct one- to two-day field reviews with staff to discuss locations of interest.
- Roadsoft - As part of its local safety efforts, MDOT supported the expansion of a GIS-based roadway management system known as Roadsoft. Among many other features and functions, Roadsoft provides local agencies timely crash data, as well as tools to analyze crash trends and diagnose crash patterns.
- Region-Specific Spreadsheets - As an early adopter of the Highway Safety Manual (HSM), MDOT participated in AASHTO's HSM Lead State Initiative, which encouraged highway agencies to use the HSM. As part of this initiative, MDOT developed an implementation plan for the HSM that included the regional calibration of predictive spreadsheets and Safety Performance Functions (SPFs) - equations that estimate expected average crash frequency as a function of traffic volume and roadway characteristics.
- Crash Reporting - In addition to the Local Safety Initiative, MDOT has also taken steps to address the quality of the crash collected on local and State-owned roadways. MDOT provides input into the Michigan State Police's training programs and materials to ensure quality reporting. Through the program, MDOT is able to emphasize what elements of crash reporting are of particular importance and how exactly they should be documented in the system.
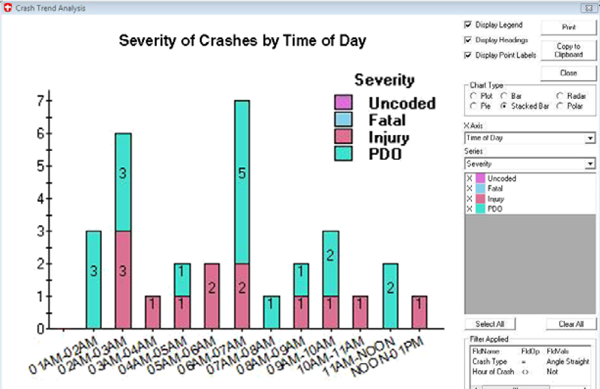
Figure 1: Roadsoft's safety analysis tools allow users to visualize trends in roadway safety. (Courtesy of MDOT)
Benefits
Local agencies have a greater understanding of the impact of quality roadway safety data on local road safety. These initiatives help bolster the State's multifaceted roadway safety program by providing local agencies with meaningful, timely access to crash data, as well as tools for data analysis and training to manage their safety processes.
Publication Year: 2014
Return to your Search Results
Return to Search page
Search the Noteworthy Practices database
|
