← Return to Monthly Spotlight Archives
Intersection Safety | April 2022
In 2020, fatalities at intersections made up nearly a third of all motor vehicle fatalities and serious injuries in Massachusetts.1 Additionally, more than 27% of all non-motorist fatalities and serious injuries occurred at intersections (“Marked crosswalks at intersection” or “At intersection but no crosswalk”).2 In recognition of the safety issues at intersections, Massachusetts Department of Transportation (MassDOT) has taken several steps to increase safety at intersections including selecting appropriate countermeasures through the adoption of Intersection Control Evaluations (ICE) and piloting the Safe System for Intersection (SSI) methodology. Additionally, MassDOT has also developed comprehensive guidelines for select intersection alternatives.
To help reduce fatalities at intersections, in 2021 MassDOT implemented the Federal Highway Administration’s (FHWA) ICE framework, a three-stage approach to develop traffic control alternatives for intersections (see Figure 1). ICE considers potential safety impacts, operational impacts, and multimodal factors for each alternative. The result of the ICE procedure is a lifecycle cost for each feasible intersection control strategy.
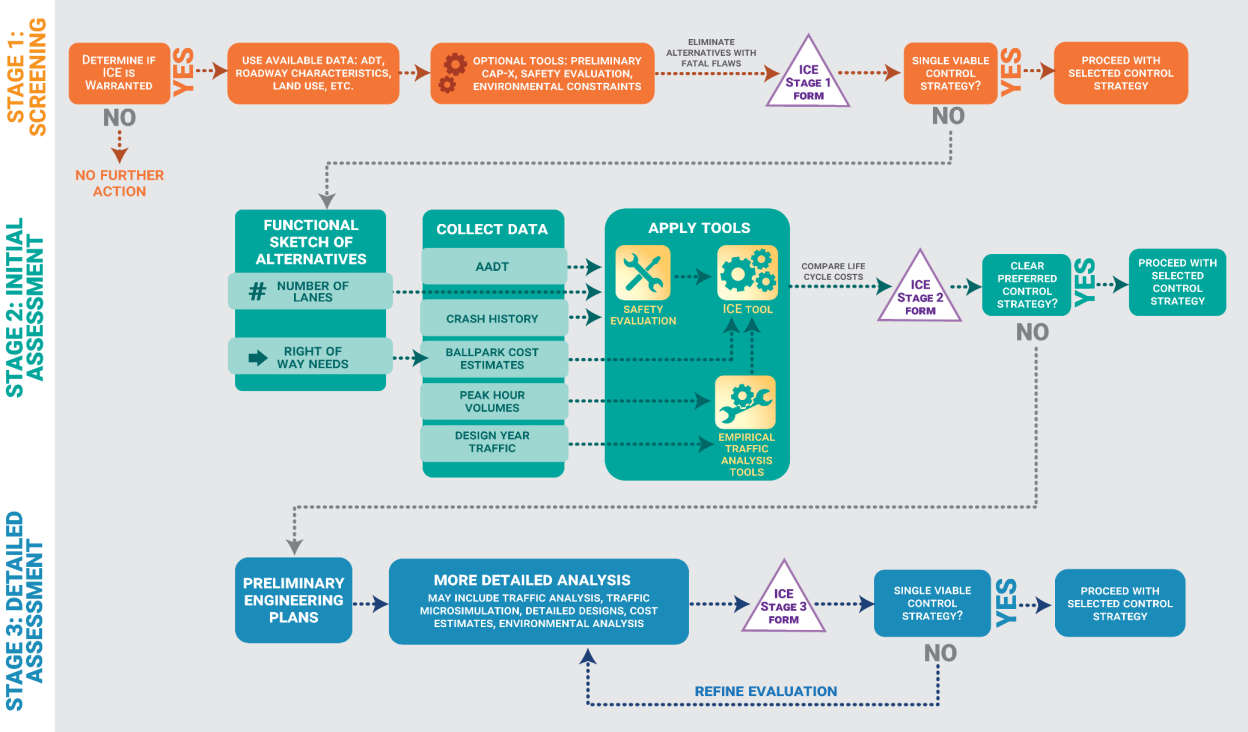
Figure 1. ICE Process Diagram
Source: MassDOT
“The SSI method, along with other approaches such as road safety audits and video analytics using drone technology, can help us gain a more complete safety performance picture to help us identify a preferred alternative that reduces risk and minimizes the potential for harm.”
-Bonnie Polin, MassDOT State Safety Engineer
Additionally, in 2021, MassDOT piloted other intersection assessment methodologies, including the SSI, for alternative analyses for intersections that were atypical and did not have safety performance functions that could be used in the ICE tool. The SSI methodology was used as an additional metric to inform alternative analysis and identify optimal improvements for an intersection. The overall framework and components of the SSI method are based on conflict point identification and classification, exposure, severity, and complexity. With these inputs, it is possible to quantify the degree to which a given intersection alternative is consistent with Safe System principles and then contrast different alternatives. The SSI methodology can also be used as a complement to video analytics and a road safety audit to get a fuller understanding of an intersection and select an effective design alternative to enhance safety.
To aid in ensuring selected alternatives are properly planned, designed, and constructed, MassDOT has developed guidelines. Of note, MassDOT published in 2020, a comprehensive guide book on the planning, outreach, analysis, design, and construction of roundabouts.
While it is still early to see quantifiable results from the implementation of ICE and piloting SSI, MassDOT has identified, through the SSI pilot, a need to revise their network screening to more heavily weigh crash severity to focus intersection improvement efforts more on reducing fatalities and serious injuries. By leveraging these new and innovative approaches demonstrates MassDOT’s commitment to improve intersection safety.
MassDOT Intersection Control Evaluation (ICE)
MassDOT Alternatives Analysis Guide
MassDOT Guidelines for the Planning and Design of Roundabouts
Roundabouts Proven Safety Countermeasure
RSPCB Program Point of Contact
Felix Delgado, FHWA Office of Safety
Felix.Delgado@dot.gov
FHWA Office of Safety
Staff and Primary Work Responsibilities
FHWA Office of Safety
Safety and Design Team
FHWA Resource Center