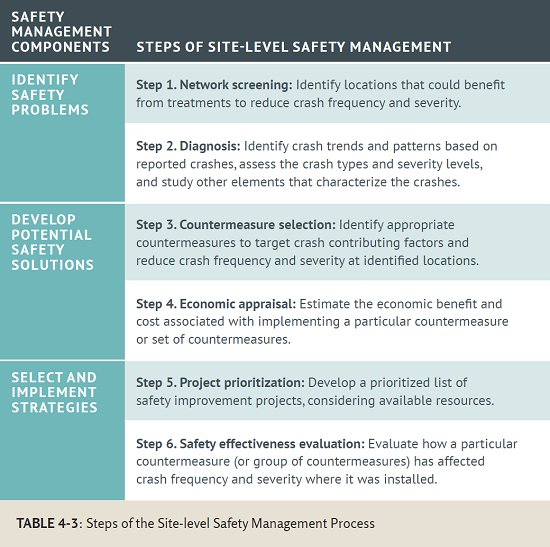
| Safety Management Components | Steps of Site-level Safety Management |
|---|---|
| Identify Safety Problems | Step 1. Network screening: Identify locations that could benefit from treatments to reduce crash frequency and severity. |
| Step 2. Diagnosis: Identify crash trends and patterns based on reported crashes, assess the crash types and severity levels, and study other elements that characterize the crashes. | |
| Develop Potential Safety Solutions | Step 3. Countermeasure selection: Identify appropriate countermeasures to target crash contributing factors and reduce crash frequency and severity at identified locations. |
| Step 4. Economic appraisal: Estimate the economic benefit and cost associated with implementing a particular countermeasure or set of countermeasures. | |
| Select and Implement Strategies | Step 5. Project prioritization: Develop a prioritized list of safety improvement projects, considering available resources. |
| Step 6. Safety effectiveness evaluation: Evaluate how a particular countermeasure (or group of countermeasures) has affected crash frequency and severity where it was installed. |
RSPCB Program Point of Contact
Felix Delgado, FHWA Office of Safety
Felix.Delgado@dot.gov
FHWA Office of Safety
Staff and Primary Work Responsibilities
FHWA Office of Safety
Safety and Design Team
FHWA Resource Center